The desert Southwest encompasses an immense area. While the desert offers many opportunities, it’s an unforgiving environment to the unprepared. Always tell a friend or relative when and where you’re going and when you plan to return.
Clothing requirements vary with the season and elevation. Lightweight light-colored clothing that fully covers the body provides protection from the sun and lessens dehydration during the hotter months. Footwear should be lightweight, durable, comfortable, and protect the ankles. Other necessities include wool outdoor socks, a wide-brimmed hat, and work gloves. A layered approach consisting of several lighter garments offers the most versatility in the winter. Include a lightweight water-repellent windbreaker. Water-repellent footwear helps prevent fungal infections and frostbite.
Keep a survival kit with you. Randall’s Adventure and Training/ESEE Knives offers several excellent survival kits.
Sonoran Desert approximately 30 miles west of Maricopa, Arizona. During the 1850s and 1860s, Maricopa Wells became a major stagecoach relay station. Photo: Highqueue, via Wikipedia
Table of Contents
MOVING ON FOOT IN THE DESERT
A topographic map of the area is a must, along with water containers, sheath knife, at least 30 feet of 550 cord, a firearm and ammunition, cell phone, and any required medications. Study the map before traveling into unfamiliar territory. Pay attention to the terrain features, roads, directions to nearest habitation, locations of water, and other important information. At your campsite, orient yourself with prominent landmarks.
When traveling away from camp, look behind often and make a mental picture of the features. Stay on established trails if possible. Take into consideration the position of the sun and shadows and where they’ll be when you plan to return. Move from one easily recognizable terrain feature to another. Mark your trail using rocks placed in the shape of arrows or with sticks stuck into the ground in your direction of travel.
Flat Iron Peak in Superstition Mountains as seen from Lost Dutchman State Park in Arizona. Legendary Lost Dutchman Gold Mine is believed to be in these mountains, but many people have disappeared while looking for it. Photo: Doug Dolde, via Wikipedia
If lost, stop and think for a moment. Ask yourself how long it has been since you last knew your position. It’s often best to stay where you are and let others find you by building a signal fire. Three fires in a triangle are the international signal for help. A signal mirror can be seen for over ten miles on a clear day. If necessary, you can improvise one from a shiny can lid or aluminum foil.
Signals made by sound are the least effective. Sound carries best just before dark. The standard distress signal is three blasts of sound—a car horn, firearm, whistle, etc.
Move with a purpose. Conserve energy. Rest every ten minutes. Go around obstacles, not over them. Adjust the rate of travel to that of the slowest individual in your party. When it’s hot, travel late in the day or early in the morning. Spend mid-day resting in any available shade. Travel at night if the terrain permits you to do so safely. Cooler temperatures will lessen dehydration and help conserve water supplies. Pick the easiest and safest route.
During rest stops, unlace your footwear and adjust your socks. Don’t remove your footwear unless you can keep your feet elevated and out of the sun. Swelling may make it difficult to put your footwear back on.
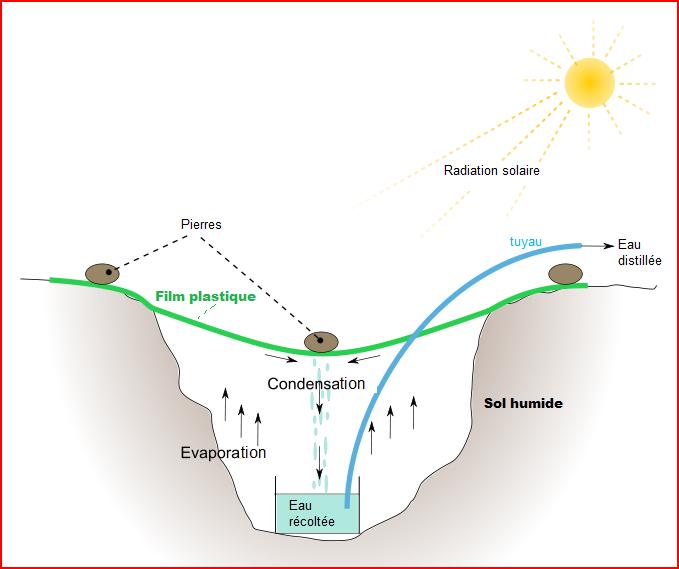
Solar still is simple way of distilling water using sun’s heat. Illustration: Smack and Happyrabbit, via Wikipedia
VEHICLE KIT
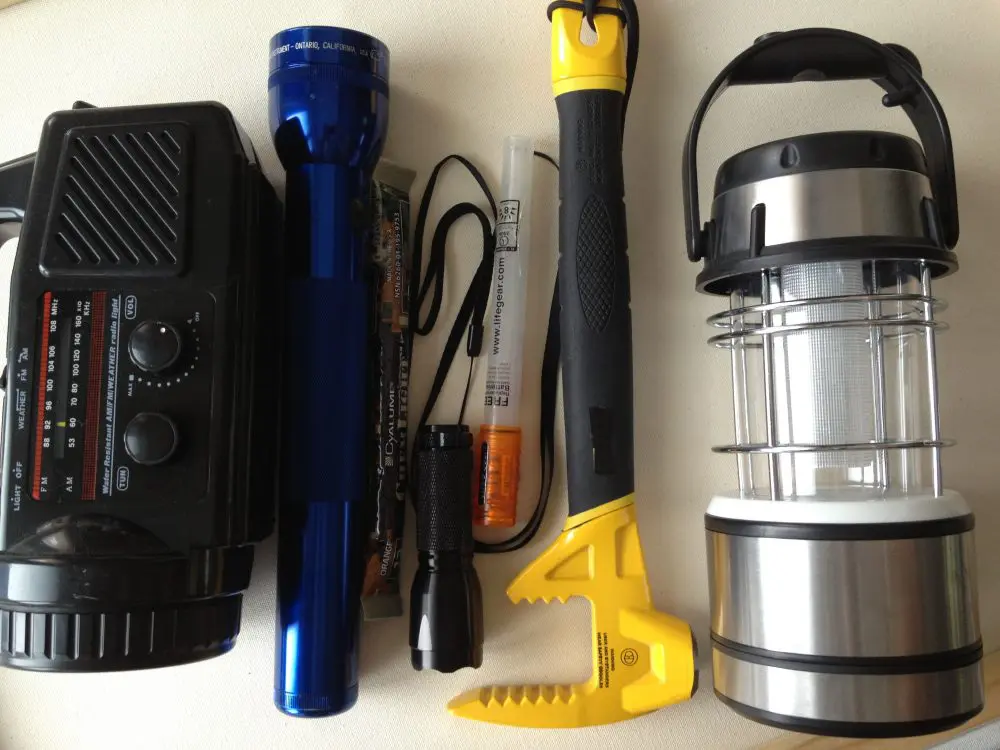
Many items that you have in your home for a natural disaster should also be in your vehicle: food, water, bedding, cooking gear, eating utensils, can opener, first aid kit, flashlight with batteries, lantern with fuel or batteries, soap, towels, toilet paper, matches, old newspapers, etc. Inspect your vehicle before traveling in the desert. Top off the gas tank. Check the cooling system, battery and oil. Spare belts and hoses are good ideas, as is a roll of duct tape.
When driving off road, have one or more shovels, a tire pump, axe, pick-mattock, tow chain or cable, full water and gas cans, at least 50 feet of ¾-inch nylon rope, and a basic tool kit. If you have enough space, a handyman high-lift jack can be extremely helpful.
Survival kit is a must any time you travel off the beaten path. This excellent pocket survival kit from Randall’s Adventure & Training is compact and lightweight. Photo: Randall’s Adventure & Training
FINDING WATER
In a survival situation, if you’re near water, stay where you are. If no water is available, look for it. Desert trails may lead to water or civilization. Pay particular attention to trails that join together and travel downward toward a specific location.
Look for water in the waste rock at the base of cliffs or gravel of washes coming from the mountain valleys that get seasonal rain. Springs can be found along the sides and floors of valleys. Lava and limestone have more springs than any other types of rock. Cold-water springs are the safest to drink from.
Water may often be found below the surface of dry streambeds at the lowest point on the outside of bends in the stream channel. Dig until you reach wet sand. Water will seep into the hole. The activities of animals may also indicate where water can be found. Flocks of birds will often circle over water holes. Doves fly toward water morning and evening.
Look for plants that only grow where there’s water, such as willows, sycamores, cottonwoods, hackberry, salt cedar, arrow weed and cattails. Many plants, such as ripe cactus fruits, can be eaten or chewed to help prevent dehydration. The immature flower stalks of yucca, agave and sotol contain moisture, and their pith can be chewed. The pith of most cacti contains moisture but it also contains oxalic acid and other substances which can cause serious medical issues. For this reason, and contrary to TV and movies, most cacti are not a source of water.
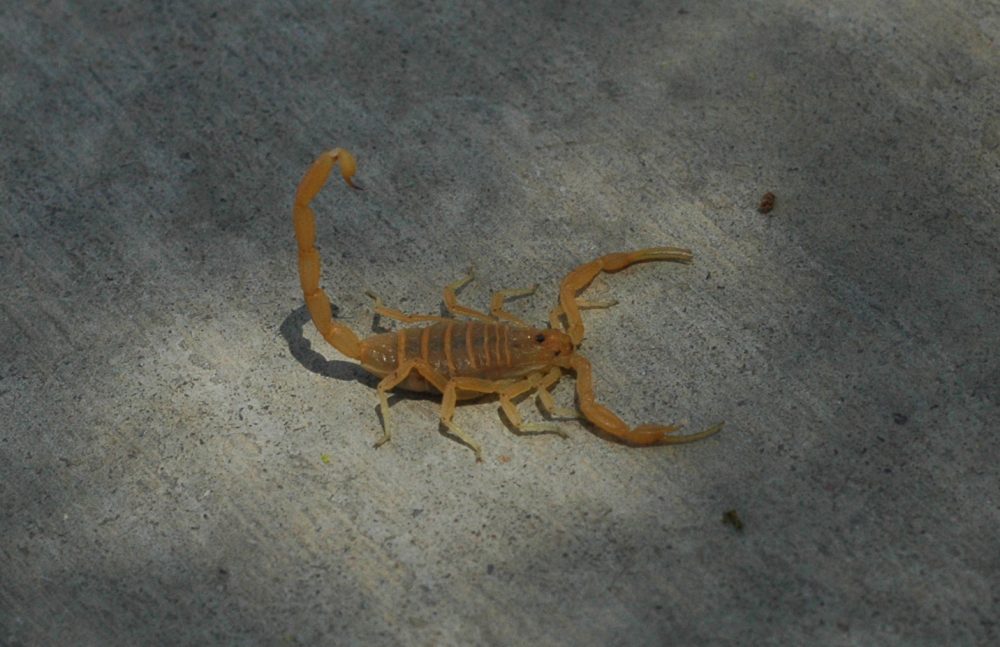
Small light brown Arizona bark scorpion is common to Southwest United States. Adult male can reach 3.14 inches in length, while female is slightly smaller, with a maximum length of 2.75 inches. Photo: Brian Basgen, via Wikipedia
Solar Stills
Water can be obtained in even the driest desert areas through the use of a solar still. The two basic types of solar stills are box and pit stills. Several solar stills are necessary to provide adequate water for one person. The basic requirement is a six-foot-diameter sheet of thin, rough-surfaced plastic (water droplets won’t adhere to smooth plastic). Place the rough side down and use a wide-mouthed container to collect the distilled water.
A solar still needs full sunlight. Two to three pints of water may be obtained from a single still per day at sites with indications of water. You can break up cacti and other plants with a high moisture content and place them in the pit to increase the recovery rate. Non-potable water can be poured into a trench around the inside of the pit and distilled for safe drinking.
Water that has not been distilled should always be filtered and purified before drinking. Filter water through several layers of cloth to remove particulate matter, though this does not kill pathogens. Purify water with water purification tablets, tincture of iodine, boiling, or solar water disinfection.
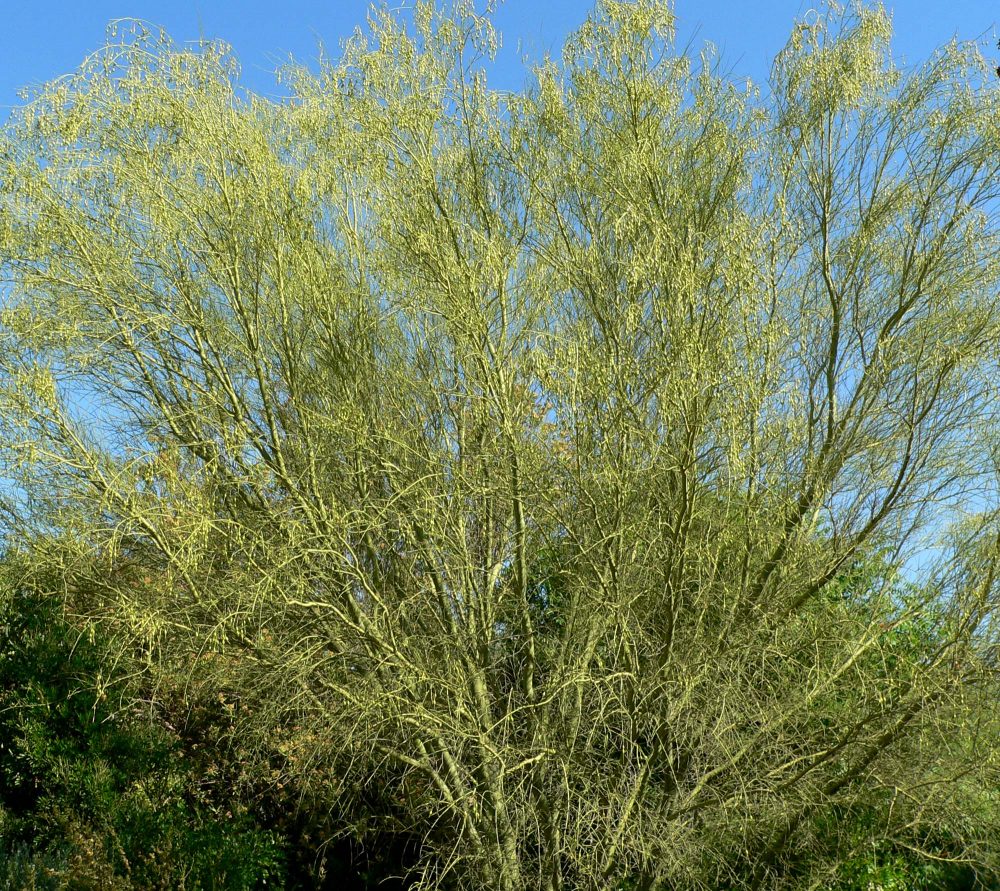
State tree of Arizona, Palo Verde produces edible beans that Native Americans collected and ground for flour. Photo: Stan Shebs, via Wikipedia
NAVIGATION
A GPS doesn’t eliminate the need for a compass. An analog watch, the sun, stars, shadows, and even nature can also guide you. To orient and use your compass, hold it horizontally and turn it so the pointer on the dial and the north mark on the compass bezel coincide. Keep the compass away from any iron or steel and allow the pointer to come completely to rest. Determine the direction to a prominent terrain feature in the direction of travel.
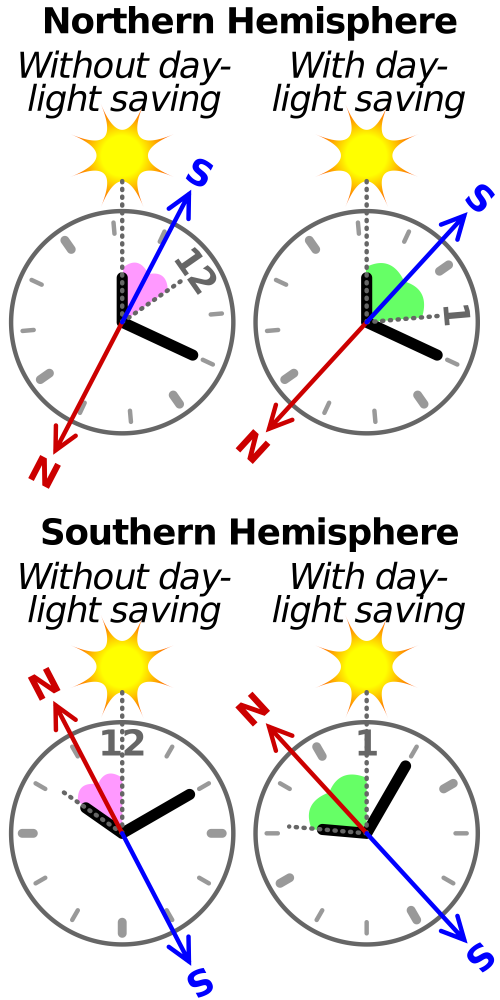
The sun is an excellent navigation tool. Stand with your right hand to the morning sun or your left hand to the evening sun and you’re facing north. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you hold your watch horizontally and point the hour hand at the sun, south will roughly be midway in the smallest angle between the hour hand and 12. At night, you can determine directions from Polaris (the North Star). Learn to recognize it and the pointer stars that help locate it.
Having the right tools is essential. ESEE 6 is a great wilderness survival knife that can handle most any task. Photo: Randall’s Adventure & Training
Never travel during storms. Mark your direction of travel and seek shelter. Dust storms can be seen long before they reach your location. If caught in a dust storm while on foot, lie down with your back to the wind and cover your head with a cloth. Whether on foot or in a vehicle, stay out of washes and gullies if a rainstorm is on the horizon.
Quicksand (fine-grain sand plus water) may occur in riverbeds, washes, and the run-off areas of recent flash floods. The surface may look like dry sand, but it acts like thick liquid. If caught in quicksand, don’t struggle. Throw yourself on your back. You’ll float. Quickly remove any equipment and spread your arms on the surface. Roll slowly to firmer ground or turn on your stomach and do a slow breaststroke. If you move slowly and carefully, you’ll easily be able to swim to safety.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONCERNS
Don’t remove your clothing in an attempt to keep cool, since this will hasten dehydration. The human body requires two to three times more water in the desert than it does in a tropical environment. Thirst is not an accurate indicator of dehydration. Fluid needs can vary based on individual differences as well as exertion. Hourly fluid intake shouldn’t exceed 1½ quarts. Daily intake shouldn’t exceed 12 quarts. Avoid smoking, coffee and alcohol, which increase dehydration.
Be alert for the initial signs and symptoms of dehydration. Ration sweat, not water. Heat cramps result from a water-to-sodium imbalance in the body and generally occur in the arms, legs or abdomen. Drink water and rest. Gentle, steady stretching and direct pressure on the cramping muscle(s) may help.
Heat exhaustion isn’t life threatening but may progress to heatstroke if left untreated. The signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion include profuse sweating, weakness, dizziness, and headache. The skin will be moist, clammy, and pale. Breathing may be rapid and shallow. A victim of heat exhaustion should rest in the shade with legs elevated. Water should be given if the victim is conscious.
Heatstroke is a life-threatening medical emergency. The skin will be flushed to red in color and usually hot and dry. The victim will be disoriented and confused and may lose consciousness. Pulse will be rapid and body temperature elevated and rising. Brain damage can occur if the body temperature isn’t lowered. Cool the victim immediately to 102°F and monitor closely. Summon emergency medical assistance as soon as possible.
Winter brings the risk of hypothermia. Signs and symptoms include shivering, weakness, loss of coordination, and difficulty performing tasks and making decisions. Shivering stops as hypothermia progresses. Unconsciousness and death eventually result.
Protect the victim from further heat loss. Shelter from wind and water. Replace wet clothing with dry and cover the head. If the signs and symptoms are mild, heat may be added to the neck, armpits and groin. If moderate to severe, prevent further heat loss and seek medical assistance for re-warming.
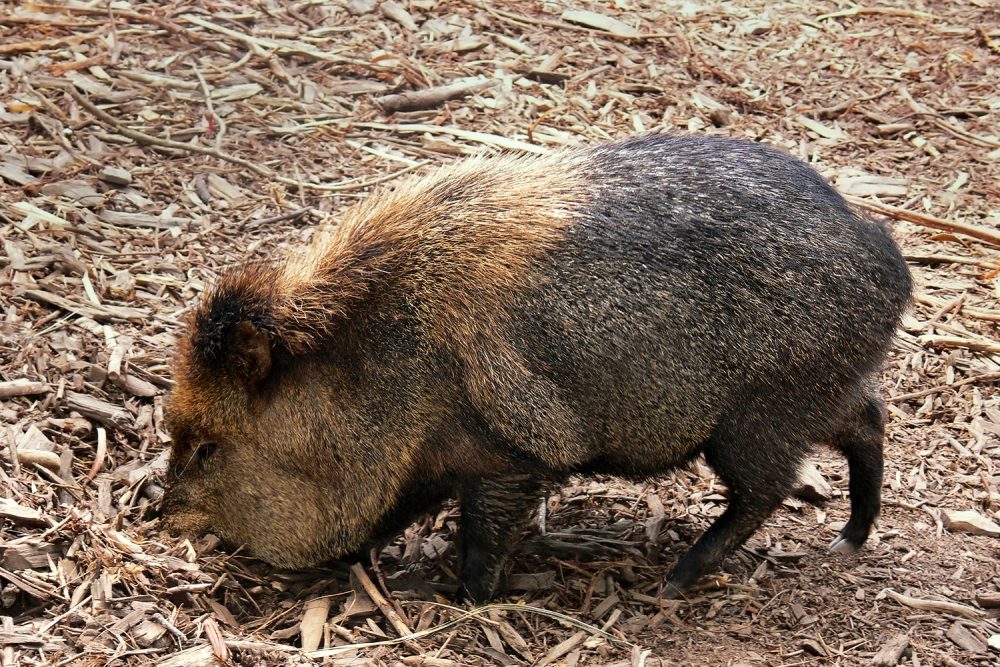
Wildlife such as javelina abounds in Arizona desert. Javelina are also called skunk pigs due to their nasty-smelling scent glands. Photo: Benjamit444, via Wikipedia
NATURE’S BUFFET
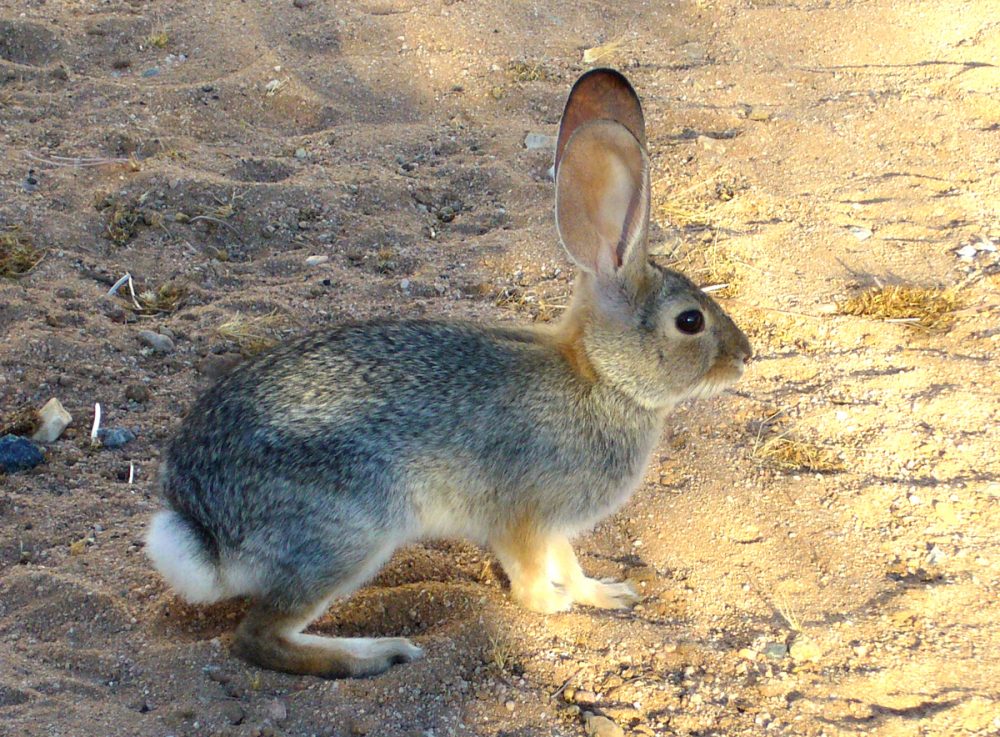
Most animals, reptiles and many insects and plants in the desert Southwest can be eaten. Learn what foods are available, how to obtain them, and how to prepare them in a survival situation. Be aware that eating increases your need for water. If water isn’t available, don’t eat. Small mammals, especially rabbits and rodents, often carry tularemia, a disease that is transmittable to humans. If an animal appears sick, don’t eat it. A spotted liver in an animal is also an indicator of the disease. Thoroughly cook meat. Some animals may have grubs in the hide or flesh, but these don’t affect the food value of the meat. Animals such as javelina have scent glands that must be removed prior to cooking.
Insects are an excellent source of fat and protein but must be cooked to kill parasites. Locusts, grasshoppers, and crickets are abundant and tasty. Don’t eat hairy caterpillars—they may be poisonous.
Preserve surplus meat by drying. Jerky can be made from the fat-free meat of large animals. Slice the meat into strips about one inch thick and several inches wide. Hang the meat in the sun for two or three days until it’s completely dry. Meat can also easily be smoke dried. Lay ¼-inch thick strips of meat on a lattice about three feet above a slow-burning fire. Don’t let the fire become hot enough to cook the meat or draw juices. Smoke the meat until it becomes brittle. Oily or pitchy woods impart an undesirable flavor to the meat.
Desert Cottontail on alert. Small mammals may have tularemia, a serious infectious disease that can be fatal if untreated. Photo: Jessie Eastland aka Robert DeMeo, via Wikipedia
Learn to construct snares, traps and deadfalls. While not as effective or selective as a firearm, they are easy to construct and may provide the only means of obtaining meat if you lack ammunition.
Desert cacti fruits can be eaten. Singe ripe fruits over fire to remove the spines before peeling and eating. The seeds of old cactus fruits can be pounded between rocks into powder that can be eaten dry or mixed with water to form gruel. Eat young pads of the prickly pear cactus after you singe, peel and boil them.
The beans of the ironwood, Palo Verde, cat claw acacia, and honey and screw bean mesquites are edible. Their fernlike leaves may identify the trees. When green and tender, the bean pods can be boiled and eaten. Mature beans must be crushed in order to be digested. You can also eat the roots of the night-blooming cereus, which is found growing near bushes and trees and looks like a cluster of old sticks. Eat the root raw or sliced and fried.
The fruits of the squawberry, hackberry, and jojoba are all edible. The young bark of the cottonwood, aspen, spruce and pine may be eaten. Pine nuts are a highly prized food. Acorns can be eaten after boiling for approximately two hours to remove the tannins. In less arid areas, cattails, burdock, dandelions, dock, lambs quarters, Miner’s lettuce, and watercress provide a delicious meal.
Many desert plants are poisonous. Avoid eating any plant unless you are sure it is edible. Don’t eat any unknown plants with a milky sap or red beans. Boil questionable plants and test them by holding a small quantity in your mouth for a few minutes. If there’s a bitter, nauseating or burning taste, don’t eat them. Only eat mushrooms you can positively identify as edible. Even mushroom experts have been fooled on occasion.
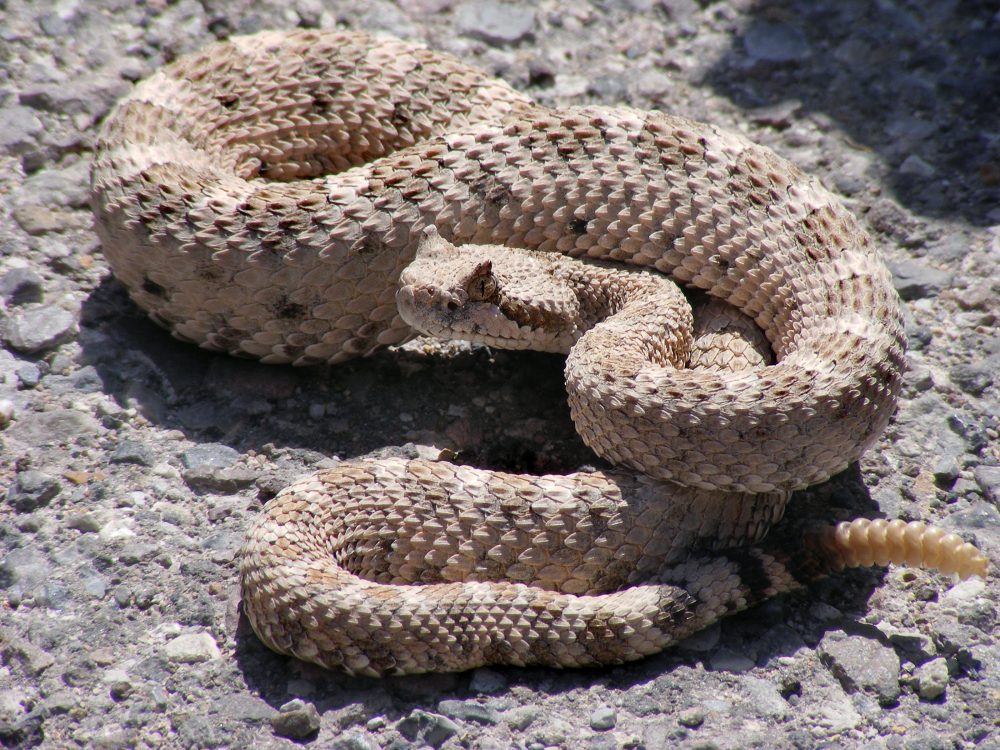
Rattlesnakes such as the horned rattlesnake—aka the Sidewinder—are common in the desert Southwest. Photo: Victorrocha, via Wikipedia
BITES AND STINGS
Rattlesnakes and the coral snake are the only venomous snakes in the Southwest. Their broad, arrow-shaped head, blunt-tipped nose, and rattles on the tail identify rattlesnakes, which are most often found where food, water, and protection are available. They don’t always give warning before striking. Like all desert reptiles, rattlesnakes hibernate during colder months. In spring and fall, they are most active during the day. During summer, they come out in the evening to avoid the hot sun.
The Arizona coral snake is rarely over 20 inches in length. It has a small black head and tapering tail. The body has red and black bands separated by narrow yellow or white bands. Coral snakes tend to be shy, and generally come out only at night.
If bitten by a venomous snake, immobilize the affected area at or below heart level. Apply a constricting band above the bite, tight enough to slow venous circulation but not cut off arterial circulation. If you can’t feel a pulse below the band, it’s too tight. Keep the victim quiet and seek immediate medical attention. Identification of the species of snake will aid in medical treatment.
Desert’s beauty attracts thousands each year, but beauty can be deceptive if you’re unprepared. Photo: Santryl, via Wikipedia
The only venomous lizard native to the Southwest U.S. is the Gila Monster, which has a stout body and tail and beaded black and coral colored skin. It’s sluggish and seldom reaches over 20 inches in length. The venom is a neurotoxin that also seems to have anticoagulant properties. Treat the bite the same as a poisonous snakebite.
The Arizona bark scorpion and the black widow spider are the most dangerous small critters in the desert Southwest.
All insect bites and stings carry with them a great risk of infection. If bitten or stung by a poisonous spider, scorpion or insect, apply a constricting band above the bite or sting for five minutes only. Most don’t need medical treatment, unless the victim is a child, elderly, has heart problems, has been stung or bitten several times or on the main part of the body.
All animal bites carry the risk of infection, tetanus and rabies. Wash animal bite wounds thoroughly with soap and water, flush the bitten area and apply a dressing. Any bite on the face or neck should receive immediate medical attention.
Only a few survival basics have been touched upon here. Pursue your survival education further!
SOURCE:
RANDALL’S ADVENTURE & TRAINING
(256) 613-0372
www.jungletraining.com